LRU Cache
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the following operations: get and put.
get(key) - Get the value (will always be positive) of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1. put(key, value) - Set or insert the value if the key is not already present. When the cache reached its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting a new item.
Follow up: Could you do both operations in O(1) time complexity?
Example:
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 / capacity / );
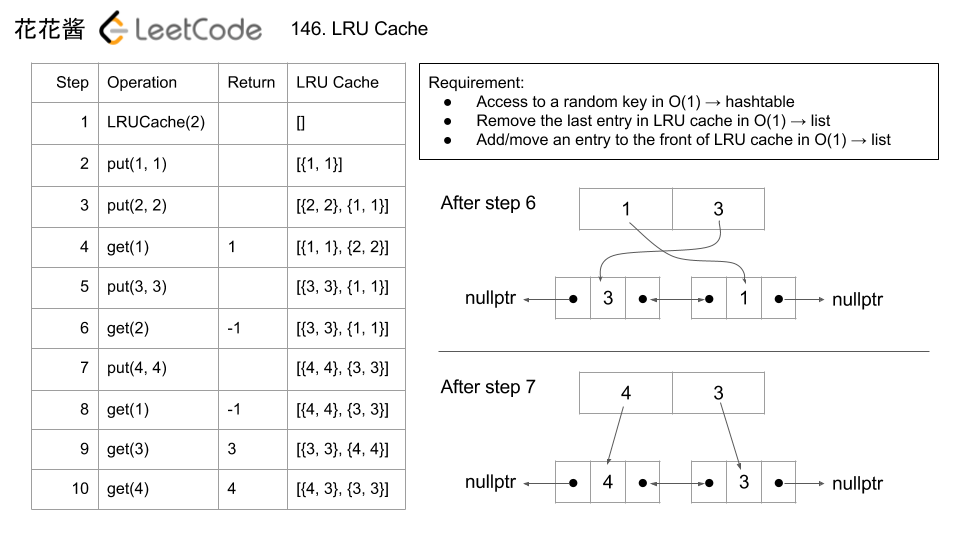
cache.put(1, 1); cache.put(2, 2); cache.get(1); // returns 1 cache.put(3, 3); // evicts key 2 cache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found) cache.put(4, 4); // evicts key 1 cache.get(1); // returns -1 (not found) cache.get(3); // returns 3 cache.get(4); // returns 4
Solution: Using hash map and list
Use Hashtable for fast mapping and double linked list for fast manipulation.
class LRUCache {
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) {
size = capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
const auto it = m.find(key);
// If key does not exist
if (it == m.end()) return -1;
// Move this key to the front of the list
// remove it->second from cache, insert it at the beginning
cache.splice(cache.begin(), cache, it->second);
return it->second->second;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
const auto it = m.find(key);
if (it != m.end()) {
// Update value is key exists
it->second->second = value;
// Move this key to the front
cache.splice(cache.begin(), cache, it->second);
return;
}
// If key doesn't exist
// If Cache is full, remove the last key
if (size == cache.size()) {
auto& node = cache.back();
m.erase(node.first);
cache.pop_back();
}
cache.emplace_front(key, value);
m[key] = cache.begin();
}
private:
int size;
unordered_map<int, list<pair<int, int>>::iterator> m;
list<pair<int, int>> cache;
};